Sterosome: An Advanced Non-Phospholipid Vesicular Drug Delivery System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.63224/tnm.2025.1.002Keywords:
Vesicular drug delivery system, Liposomes, Sterosomes, Cancer treatment, Bone regeneration, Gene delivery, Dental deliveryAbstract
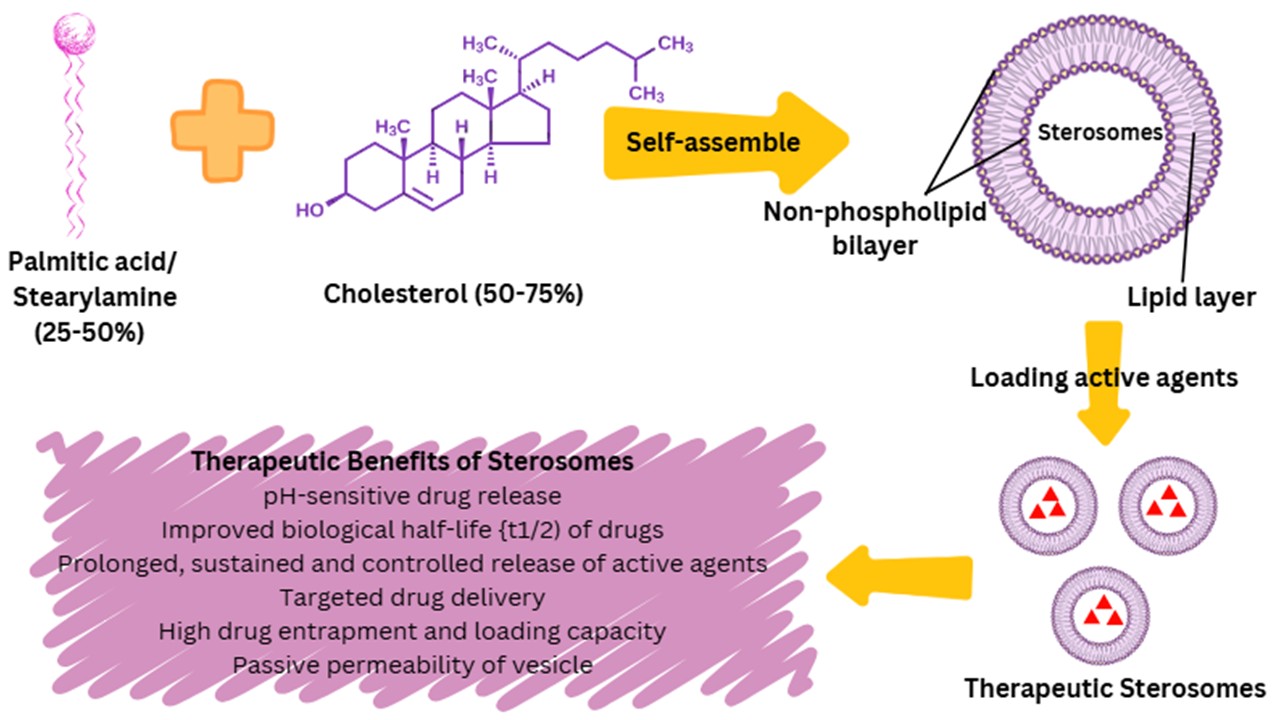
The growing number of problems linked to pharmaceuticals that have emanated from varied chemical and biological backgrounds has prompted scientists to seek out newer molecules and develop new methods and means of delivering them. Using unique drug delivery systems or techniques, both old and new compounds can be delivered to the site of need in a defined manner. Liposomes are regarded as an almost ideal drug-carrier system due to their morphology, similar to that of biological membranes, as well as their ability to incorporate drugs and transport both hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules, making them the most studied drug nanocarrier. However, liposomes face several limitations, including low encapsulation efficiencies, premature release of hydrophilic pharmaceuticals, and variable stability depending on the specific encapsulated drugs. These challenges have driven the need for modifications, leading to the development of a novel class of liposomes known as sterosomes. Sterosomes are composed of non-phospholipid, single-chain amphiphilic molecules with high sterol content, offering enhanced properties compared to conventional liposomes. At the nanoscale, sterosomes are produced as massive unilamellar vesicular systems with a diameter that can be modified based on the pore size of the filter employed in the extrusion system. They also exhibit the unique benefit of monomodal dispersion and low permeability of bilayers and have proven to be more stable than conventional liposomes. As a result, sterosomes hold significant potential to overcome the limitations associated with traditional liposomes. However, only a limited number of studies have explored their use as nanocarriers for enhancing the treatment of various diseases. Despite this, sterosomes represent a promising and innovative non-phospholipid liposomal platform for drug delivery, offering unique advantages that warrant further investigation. This review focuses on sterosomes as an emerging drug delivery system, highlighting their advantages, preparation methods, characterization techniques, and recent applications in disease treatment. In addition, it examines their inherent functionality and provides recommendations for future applications, as sterosomes have demonstrated considerable potential in addressing a wide range of diseases.
References
Ayorinde JO, Odeniyi MA, Bansal AK. Evaluation of two novel plant gums for bioadhesive microsphere and sustained-release formulations of metformin hydrochloride. Polim Med. 2017;47(1):13–23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17219/pim/74776.
Odeniyi MA, Omoteso OA, Adepoju AO, Jaiyeoba KT. Starch nanoparticles in drug delivery: A review. Polim Med. 2018;48(1):41–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17219/pim/99993.
Odeniyi MA, Adepoju AO, Jaiyeoba KT. Native and modified Digitaria exilis starch nanoparticles as a carrier system for the controlled release of naproxen. Starch‐Stärke. 2019;71(9–10):1900067. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201900067.
Okunlola A, Odeniyi MA, Arhewoh MI. Microsphere formulations of ambroxol hydrochloride: influence of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) mucilage as a sustained release polymer. Prog Biomater. 2020;9(1–2):65–80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40204-020-00132-5.
Bamiro OA, Odeniyi MA, Addo RT. Native and modified Oryza glaberrima steud starch nanocrystals: Solid-state characterization and anti-tumour drug release studies. Br J Pharm. 2021;6(1):790. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5920/bjpharm.790.
Andonova V. Synthetic polymer-based nanoparticles: intelligent drug delivery systems. In: Acrylic Polymers in Healthcare, Reddy B (Ed.); IntechOpen: India; 2017; 101–125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.69056.
Arundhasree R, Aiswarya R, Kumar AR, Kumar S, Ufasomes NS. Ufasomes: Unsaturated fatty acid based vesicular drug delivery system. Int J Appl Pharm. 2021;13(2):76–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22159/ijap.2021v13i2.39526.
Laffleur F, Keckeis V. Advances in drug delivery systems: Work in progress still needed? Int J Pharm. 2020;590:119912. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119912.
Bnyan R, Khan I, Ehtezazi T, Saleem I, Gordon S, O’Neill F, Roberts M. Surfactant effects on lipid-based vesicles properties. J Pharm Sci. 2018;107(5):1237–1246. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.01.005.
Alenzi AM, Albalawi SA, Alghamdi SG, Albalawi RF, Albalawi HS, Qushawy M. Review on different vesicular drug delivery systems (VDDSs) and their applications. Recent Pat Nanotechnol. 2023;17(1):18–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1872210516666220228150624.
Mahale NB, Thakkar PD, Mali RG, Walunj DR, Chaudhari S. Niosomes: Novel sustained release nonionic stable vesicular systems—an overview. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2012;183–184:46–54. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2012.08.002.
Kamboj S, Saini V, Magon N, Bala S, Jhawat V. Vesicular drug delivery systems: a novel approach for drug targeting. Inter J Drug Deliv. 2013;5(2):121–130.
Paré C, Lafleur M. Formation of liquid ordered lamellar phases in the palmitic acid/cholesterol system. Langmuir. 2001;17(18):5587–5594. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la0102410.
Cui ZK, Kim S, Baljon JJ, Doroudgar M, Lafleur M, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Design and characterization of a therapeutic non-phospholipid liposomal nanocarrier with osteoinductive characteristics to promote bone formation. ACS Nano. 2017;11(8):8055–8063. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b02702.
AbouSamra MM, Afifi SM, Galal AF, Kamel R. Rutin-loaded Phyto-Sterosomes as a potential approach for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: in-vitro and in-vivo studies. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023;79:104015. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.104015.
Zhang Y, Zhou J, Wu JL, Ma JC, Wang H, Wen J, Huang S, Lee M, Bai X, Cui ZK. Intrinsic antibacterial and osteoinductive sterosomes promote infected bone healing. J Contr Rel. 2023;354:713–725. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.058.
Cui ZK, Lafleur M. Lamellar self-assemblies of single-chain amphiphiles and sterols and their derived liposomes: Distinct compositions and distinct properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;114:177–185. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.09.042.
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabady R, Davaran S, Joo SW, Zarghami N, Hanifehpour Y, Samiei M, Kouhi M, Nejati-Koshki K. Liposome: classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2013;8:1–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-102.
Torchilin VP. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4(2):145–160. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1632.
Bozzuto G, Molinari A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:975–999. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S68861.
Salimi A. Liposomes as a novel drug delivery system: fundamental and pharmaceutical application. Asian J Pharm. 2018;12(1):S31.
Mansoori M. A review on liposome. Int J Adv Res Pharm Bio Sci. 2012;2:453–464. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-4377.2015.00033.6.
Li J, Wang X, Zhang T, Wang C, Huang Z, Luo X, Deng Y. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2015;10(2):81–98. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2014.09.004.
Pattni BS, Chupin VV, Torchilin VP. New developments in liposomal drug delivery. Chem Rev. 2015;115(19):10938–10966. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00046.
Sahoo SK, Labhasetwar V. Nanotech approaches to drug delivery and imaging. Drug Discov Today. 2003;8(24):1112–1120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6446(03)02903-9.
Sercombe L, Veerati T, Moheimani F, Wu SY, Sood AK, Hua S. Advances and challenges of liposome assisted drug delivery. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6:286. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00286.
Noble GT, Stefanick JF, Ashley JD, Kiziltepe T, Bilgicer B. Ligand-targeted liposome design: challenges and fundamental considerations. Trends Biotechnol. 2014;32(1):32–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.09.007.
Vijay KS, Mishra D, Sharma A, Srivastava B. Liposomes: present prospective and future challenges. Int J Curr Pharm Rev Res. 2010;1(2):6–16.
Longmire M, Choyke PL, Kobayashi H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: considerations and caveats. Nanomed. 2008;4(3):245–257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2217/17435889.3.5.703.
Gaspar MM, Bakowsky U, Ehrhardt C. Inhaled liposomes–current strategies and future challenges. J Biomed Nanotech. 2008;4(3):245–257. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2008.334.
Moghimi SM, Farhangrazi ZS. Nanomedicine and the complement paradigm. Nanomedicine Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2013;9(4):458–460. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2013.02.011.
Charrois GJ, Allen TM. Rate of biodistribution of STEALTH® liposomes to tumor and skin: influence of liposome diameter and implications for toxicity and therapeutic activity. BBA-Biomembranes. 2003;1609(1):102–108. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2736(02)00661-2.
Li SD, Huang L. Stealth nanoparticles: high density but sheddable PEG is a key for tumor targeting. J Contr Rel. 2010;145(3):178–181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.03.016.
Kong M, Hou L, Wang J, Feng C, Liu Y, Cheng X, Chen X. Enhanced transdermal lymphatic drug delivery of hyaluronic acid modified transfersomes for tumor metastasis therapy. Chem Comm. 2015;51(8):1453–1456. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC08746A.
Andra VVSNL, Pammi SVN, Bhatraju LVKP, Ruddaraju LK. A comprehensive review on novel liposomal methodologies, commercial formulations, clinical trials and patents. Bionanosci. 2022;12:274–291. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-022-00941-x.
Jafari A, Daneshamouz S, Ghasemiyeh P, Mohammadi-Samani S. Ethosomes as dermal/transdermal drug delivery systems: applications, preparation and characterization. J Liposome Res. 2023;33:34–52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2022.2085742.
Salama AH, Aburahma MH. Ufasomes nano-vesicles-based lyophilized platforms for intranasal delivery of cinnarizine: preparation, optimization, ex-vivo histopathological safety assessment and mucosal confocal imaging. Pharm Dev Technol. 2016;21(6):706–715. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3109/10837450.2015.1048553.
Bhardwaj P, Tripathi P, Gupta R, Pandey S. Niosomes: A review on niosomal research in the last decade. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2020;56:101581. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.101581.
Fatima I, Rasul A, Shah S, Saadullah M, Islam N, Khames A, Salawi A, Ahmed MM, Almoshari Y, Abbas G, Abourehab MA. Novasomes as nano-vesicular carriers to enhance topical delivery of fluconazole: A new approach to treat fungal infections. Mol. 2022;27(9):2936. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27092936.
Cui ZK, Bouisse A, Cottenye N, Lafleur M. Formation of pH-sensitive cationic liposomes from a binary mixture of monoalkylated primary amine and cholesterol. Langmuir. 2012;28:13668–13674. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la302278q.
Cui ZK, Fan J, Kim S, Bezouglaia O, Fartash A, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Delivery of siRNA via cationic Sterosomes to enhance osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Contr Rel. 2015;217:42–52. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.08.031.
Osama H, Sayed OM, Hussein RR, Abdelrahim M, Elberry AA. Design, optimization, characterization, and in vivo evaluation of sterosomes as a carrier of metformin for treatment of lung cancer. J Liposome Res. 2020;30(2):150–162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2019.1610434.
Cui ZK, Bastiat G, Jin C, Keyvanloo A, Lafleur M. Influence of the nature of the sterol on the behavior of palmitic acid/sterol mixtures and their derived liposomes. BBA-Biomembranes. 2010;1798(6):1144–1152. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.02.008.
Ouimet J, Lafleur M. Hydrophobic match between cholesterol and saturated fatty acid is required for the formation of lamellar liquid ordered phases. Langmuir. 2004;20(18):7474–7481. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la0491293.
Carbajal G, Cui ZK, Lafleur M. Non-phospholipid liposomes with high sterol content display a very limited permeability. Sci China Chem. 2013;56:40–47. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4775-7.
Bastiat G, Lafleur M. Phase behavior of palmitic acid/cholesterol/cholesterol sulfate mixtures and properties of the derived liposomes. J Phy Chem B. 2007;111(37):10929–10937. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0715833.
Phoeung T, Aubron P, Rydzek G, Lafleur M. pH-triggered release from nonphospholipid LUVs modulated by the p K a of the included fatty acid. Langmuir. 2010;26(15):12769–12776. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la1014829.
Cui ZK, Edwards K, Orellana AN, Bastiat G, Benoit JP, Lafleur M. Impact of interfacial cholesterol-anchored polyethylene glycol on sterol-rich non-phospholipid liposomes. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;428:111–120. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.04.031.
Cottenye N, Carbajal G, Cui ZK, Ducharme PD, Mauzeroll J, Lafleur M. Formation, stability, and pH sensitivity of free-floating, giant unilamellar vesicles using palmitic acid–cholesterol mixtures. Soft Matter. 2014;10(34):6451–6456. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C4SM00883A.
Cieślak A, Wauthoz N, Orellana AN, Lautram N, Béjaud J, Hureaux J, Lafleur M, Benoit JP, Salomon CJ, Bastiat G. Stealth nanocarriers based sterosomes using PEG post-insertion process. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;115:31–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.02.008.
Linsley CS, Zhu M, Quach VY, Wu BM. Preparation of photothermal palmitic acid/cholesterol liposomes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(5):1384–1392. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.34230.
Cui ZK, Sun JA, Baljon JJ, Fan J, Kim S, Wu BM, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Simultaneous delivery of hydrophobic small molecules and siRNA using Sterosomes to direct mesenchymal stem cell differentiation for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2017;58:214–224. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2017.05.057.
Nwabuife JC, Hassan D, Pant AM, Devnarain N, Gafar MA, Osman N, Rambharose S, Govender T. Novel vancomycin free base–Sterosomes for combating diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections (S. Aureus and MRSA). J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023;79:104089. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.104089.
Cui ZK, Bastiat G, Lafleur M. Formation of fluid lamellar phase and large unilamellar vesicles with octadecyl methyl sulfoxide/cholesterol mixtures. Langmuir. 2010;26(15):12733–12739. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la100749k.
Phoeung T, Huber LM, Lafleur M. Cationic detergent/sterol mixtures can form fluid lamellar phases and stable unilamellar vesicles. Langmuir. 2009;25(10):5778–5784. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la804222w.
Cottenye N, Cui ZK, Wilkinson KJ, Barbeau J, Lafleur M. Interactions between non-phospholipid liposomes containing cetylpyridinium chloride and biofilms of Streptococcus mutans: modulation of the adhesion and of the biodistribution. Biofouling. 2013;29(7):817–827. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2013.807505.
Yang X, Zhan C, Cheng T, Huang M, Ge W, Zhang Y, Chen T, Lu Y, Cui ZK, Hou J. Evaluation of the transdentinal capability of the intrinsic antibacterial cetylpyridinium chloride/cholesterol sterosomes in vitro and in vivo. Int Endod J. 2023;56(2):245–258. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.13865.
Gater DL, Seddon JM, Law RV. Formation of the liquid-ordered phase in fully hydrated mixtures of cholesterol and lysopalmitoylphosphatidylcholine. Soft Matter. 2008;4(2):263–267. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/B710726A.
Ramakrishnan M, Tarafdar PK, Kamlekar RK, Swamy MJ. Differential scanning calorimetric studies on the interaction of N-acylethanolamines with cholesterol. Curr Sci. 2007;93(2):234–238.
Lee CS, Kim S, Fan J, Hwang HS, Aghaloo T, Lee M. Smoothened agonist sterosome immobilized hybrid scaffold for bone regeneration. Sci Adv. 2020;6(17):eaaz7822. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz7822.
Cui ZK, Phoeung T, Rousseau PA, Rydzek G, Zhang Q, Bazuin CG, Lafleur M. Nonphospholipid fluid liposomes with switchable photocontrolled release. Langmuir. 2014;30(36):10818–10825. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/la502131h.
Patil YP, Jadhav S. Novel methods for liposome preparation. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014;177:8–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2013.10.011.
Thomas AM, Kapanen AI, Hare JI, Ramsay E, Edwards K, Karlsson G, Bally MB. Development of a liposomal nanoparticle formulation of 5-fluorouracil for parenteral administration: formulation design, pharmacokinetics and efficacy. J Contr Release. 2011;150(2):212–219. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2010.11.018.
Škalko N, Bouwstra J, Spies F, Stuart M, Frederik PM, Gregoriadis G. Morphological observations on liposomes bearing covalently bound protein: Studies with freeze-fracture and cryo electron microscopy and small angle X-ray scattering techniques. BBA-Biomembranes. 1998; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2736(97)00256-3.
Fröhlich E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:5577–5591. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S36111.
Omwoyo WN, Ogutu B, Oloo F, Swai H, Kalombo L, Melariri P, Mahanga GM, Gathirwa JW. Preparation, characterization, and optimization of primaquine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;11:3865–3874. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S62630.
Koyama TM, Stevens CR, Borda EJ, Grobe KJ, Cleary DA. Characterizing the gel to liquid crystal transition in lipid-bilayer model systems. Chem. Educ. 1999;4:12–15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00897990273a.
Gill P, Moghadam TT, Ranjbar B. Differential scanning calorimetry techniques: applications in biology and nanoscience. J Biomol Techn. 2010;21(4):167.
Watson E, O’neill M, Justin J, Brenner N. A differential scanning calorimeter for quantitative differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1964;36(7):1233–1238. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60213a019.
Bond L, Allen S, Davies MC, Roberts CJ, Shivji AP, Tendler SJ, Williams PM, Zhang J. Differential scanning calorimetry and scanning thermal microscopy analysis of pharmaceutical materials. Int J Pharm. 2002;243(1–2):71–82. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-5173(02)00239-9.
Giron D. Applications of thermal analysis and coupled techniques in pharmaceutical industry. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2002;68(2):335–357. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1016015113795.
Chauhan A, Goyal MK, Chauhan P. GC-MS technique and its analytical applications in science and technology. J Anal Bioanal Tech. 2014;5(6):222. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9872.1000222.
Macario A, Verri F, Diaz U, Corma A, Giordano GI. Pure silica nanoparticles for liposome/lipase system encapsulation: Application in biodiesel production. Catal Today. 2013;204:148–155. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2012.07.014.
Wu LP, Wang D, Li Z. Grand challenges in nanomedicine. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;106:110302. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110302.
Zhang Z, Yang J, Yang Q, Tian G, Cui ZK. Fabrication of non-phospholipid liposomal nanocarrier for sustained-release of the fungicide cymoxanil. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:627817. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2021.627817.
Verma N, Arora V, Awasthi R, Chan Y, Jha NK, Thapa K, Jawaid T, Kamal M, Gupta G, Liu G, Paudel KR. Recent developments, challenges and future prospects in advanced drug delivery systems in the management of tuberculosis. J Drug Sci Technol. 2022;75:103690. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2022.103690.
Tiwari AP, Hwang TI, Oh JM, Maharjan B, Chun S, Kim BS, Joshi MK, Park CH, Kim CS. pH/NIR-responsive polypyrrole-functionalized fibrous localized drug-delivery platform for synergistic cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(24):20256–20270. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b17664.
Deng Y, Käfer F, Chen T, Jin Q, Ji J, Agarwal S. Let there be light: Polymeric micelles with upper critical solution temperature as light‐triggered heat nanogenerators for combating drug‐resistant cancer. Small. 2018;14(37):1802420. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201802420.
Wu Y, Wang H, Gao F, Xu Z, Dai F, Liu W. An injectable supramolecular polymer nanocomposite hydrogel for prevention of breast cancer recurrence with theranostic and mammoplastic functions. Adv Funct Mater. 2018;28(21):1801000. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201801000.
Li Q, Li W, Di H, Luo L, Zhu C, Yang J, Yin X, Yin H, Gao J, Du Y, You J. A photosensitive liposome with NIR light triggered doxorubicin release as a combined photodynamic-chemo therapy system. J Contr Rel. 2018;277:114–125. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.02.001.
Pan P, Svirskis D, Rees SW, Barker D, Waterhouse GI, Wu Z. Photosensitive drug delivery systems for cancer therapy: Mechanisms and applications. J Contr Rel. 2021;338:446–461. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.053.
Shimomura M, Ando R, Kunitake T. Orientation and spectral characteristics of the azobenzene chromophore in the ammonium bilayer assembly. Ber Bunsenges Phys Chem. 1983;87(12):1134–1143. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/bbpc.19830871211.
Song X, Perlstein J, Whitten DG. Supramolecular aggregates of azobenzene phospholipids and related compounds in bilayer assemblies and other microheterogeneous media. structure, properties, and photoreactivity. J Amr Chem Soc. 1997;119(39):9144–9159. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja971291n.
Chen S, Bian Q, Wang P, Zheng X, Lv L, Dang Z, Wang G. Photo, pH and redox multi-responsive nanogels for drug delivery and fluorescence cell imaging. Polym Chem. 2017;8(39):6150–6157. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C7PY01424D.
Hu C, Ma N, Li F, Fang Y, Liu Y, Zhao L, Qiao S, Li X, Jiang X, Li T, Shen F. Cucurbit[8]uril-based giant supramolecular vesicles: highly stable, versatile carriers for photoresponsive and targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(5):4603–4613. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00297.
Razavi B, Abdollahi A, Roghani-Mamaqani H, Salami-Kalajahi M. Light-and temperature-responsive micellar carriers prepared by spiropyran-initiated atom transfer polymerization: Investigation of photochromism kinetics, responsivities, and controlled release of doxorubicin. Polym. 2020;187:122046. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.122046.
Utsugi T, Schroit AJ, Connor J, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ. Elevated expression of phosphatidylserine in the outer membrane leaflet of human tumor cells and recognition by activated human blood monocytes. Cancer Res. 1991;51(11):3062–3066.
Ejigah V, Owoseni O, Bataille-Backer P, Ogundipe OD, Fisusi FA, Adesina SK. Approaches to improve macromolecule and nanoparticle accumulation in the tumor microenvironment by the enhanced permeability and retention effect. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(13):2601. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14132601.
Adeyemi SA, Kumar P, Choonara YE, Pillay V. Stealth properties of nanoparticles against cancer: surface modification of NPs for passive targeting to human cancer tissue in zebrafish embryos. In: Surface Modification of Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery; Pathak YV (Ed.); Springer: Switzerland, 2019; 99–124. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06115-9_5.
Guido C, Maiorano G, Cortese B, D’Amone S, Palamà IE. Biomimetic nanocarriers for cancer target therapy. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(3):111. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7030111.
Sharma S, Rajendran V, Kulshreshtha R, Ghosh PC. Enhanced efficacy of anti-miR-191 delivery through stearylamine liposome formulation for the treatment of breast cancer cells. Int J Pharm. 2017;530(1–2):387–400. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2017.07.079.
Fotooh Abadi L, Damiri F, Zehravi M, Joshi R, Pai R, Berrada M, Massoud E, Rahman M, Rojekar S, Cavalu S. Novel nanotechnology-based approaches for targeting HIV reservoirs. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(15):3090. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14153090.
Savchenko IV, Zlotnikov ID, Kudryashova EV. Biomimetic systems involving macrophages and their potential for targeted drug delivery. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023;8(7):543. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8070543.
Hama S, Sakai M, Itakura S, Majima E, Kogure K. Rapid modification of antibodies on the surface of liposomes composed of high-affinity protein A-conjugated phospholipid for selective drug delivery. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021;27:101067. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101067.
Serov N, Vinogradov V. Artificial intelligence to bring nanomedicine to life. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;184:114194. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2022.114194.
Gao XJ, Ciura K, Ma Y, Mikolajczyk A, Jagiello K, Wan Y, Gao Y, Zheng J, Zhong S, Puzyn T, Gao X. Toward the integration of machine learning and molecular modeling for designing drug delivery nanocarriers. Adv Mater. 2024;36(45):2407793. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202407793.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. Omobolanle A. Omoteso, Dr. Nnamdi I. Okafor, Prof. Michael A. Odeniyi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Under the CC BY 4.0 license, copyrights are retained by the authors, and anyone can have free and unlimited access, reuse, read and download any article for free. No permission is needed to reuse any part of articles published by Trends in NanoMed (TNM), including figures and tables. However, the original source must be clearly cited.

